Learning Guides
Evidence-based study strategies from Masterful Learning. Organized from broad strategies to domain/subdomain guidance.
45 guides across 3 levels
General Strategies
Universal learning techniques that apply across all subjects.

Are equation sheets effective for math & physics? Sometimes
Equation sheets can build structure or become a lookup crutch. Learn a memory-first method that forces conditions, links principles, and speeds exam work.

Are keyword mnemonics effective for math & physics? Rarely
Keyword mnemonics tie new terms to familiar sounds and images. Good for labels, weak for problem solving in math and physics. Use deeper methods instead.

Cornell Notes: Better Than Transcription, But Not Enough
Are Cornell Notes effective? Better than standard notes, but still passive unless you use the cue column for retrieval and the summary for elaboration.

Effective Study Mindsets for Math and Physics Mastery
Effective mindsets for math and physics: study with purpose, treat difficulty as good, balance exams with mastery, and help others who want help so skill compounds.
Elaborative Encoding: Learn Faster with Better Connections
Master elaborative encoding—the study method that transforms raw input into retrievable knowledge through targeted questions, meaningful links, and prior knowledge activation.
Essential Reading List for Physics Students and Lifelong Learners
A curated collection of books spanning physics, learning science, and critical thinking - from foundational texts to cutting-edge research.

Five-Step Strategy for Problem Solving in Physics
A research-backed method for solving physics problems effectively, from decoding to reflection.

Hint and Try - Maximize Your Learning with Pretesting and Posttesting
Hint and Try blends pretesting, worked-example hints, self-explanation, and posttesting to accelerate learning without wasting time stuck or copying solutions.
How to Interleave Your Studying for Better Recall, Transfer, and Test Scores
Interleaving beats blocking. Learn what interleaving is, why it works, and exactly how to mix topics and problem types to maximize long-term learning.

Ineffective Study Techniques for Math & Physics
Most popular techniques fail in math and physics: rereading, highlighting, neat notes. Replace them with elaboration, retrieval, self-explanation, and problems.

Is Blurting Effective for Learning Math & Physics? Rarely
Blurting (brain dumping) is a popular retrieval tactic, but for math and physics it rarely builds problem-solving skill. Learn what it is, how it works, and when to skip it.
Is Memory Palace Effective for Learning Math/Physics? Rarely
Memory palaces store sequences, not relationships. For math and physics, use strategies that encode when principles apply and how to solve problems in exams.
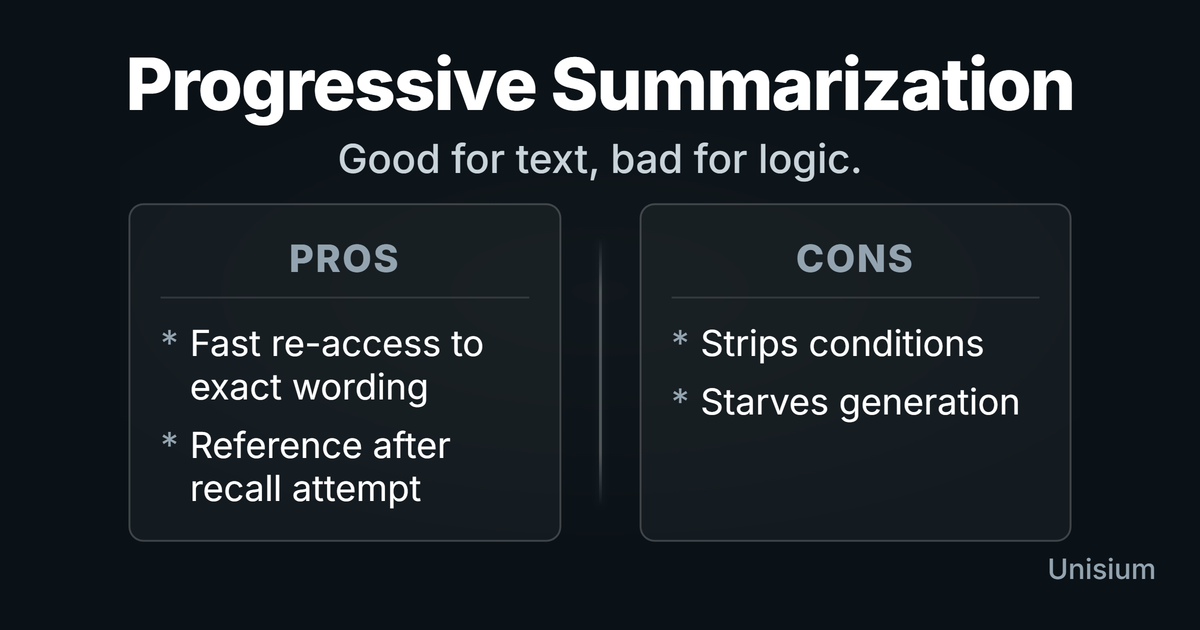
Is Progressive Summarization Effective for Learning Math & Physics? Rarely
Progressive summarization speeds up finding passages, but it weakens step-generation for math and physics. Use it only for constraints lists and decision rules.

Is Rereading Effective for Learning Math & Physics? Rarely
Rereading improves recognition, not recall, so you stall on math and physics problems under time pressure. Use retrieval, self-explanation, and spacing instead.

Is Rewriting Notes Effective for Learning Math & Physics? No
Rewriting notes is busywork: transcription without retrieval. Learn why copying fails in math and physics under time pressure, and what to do instead.
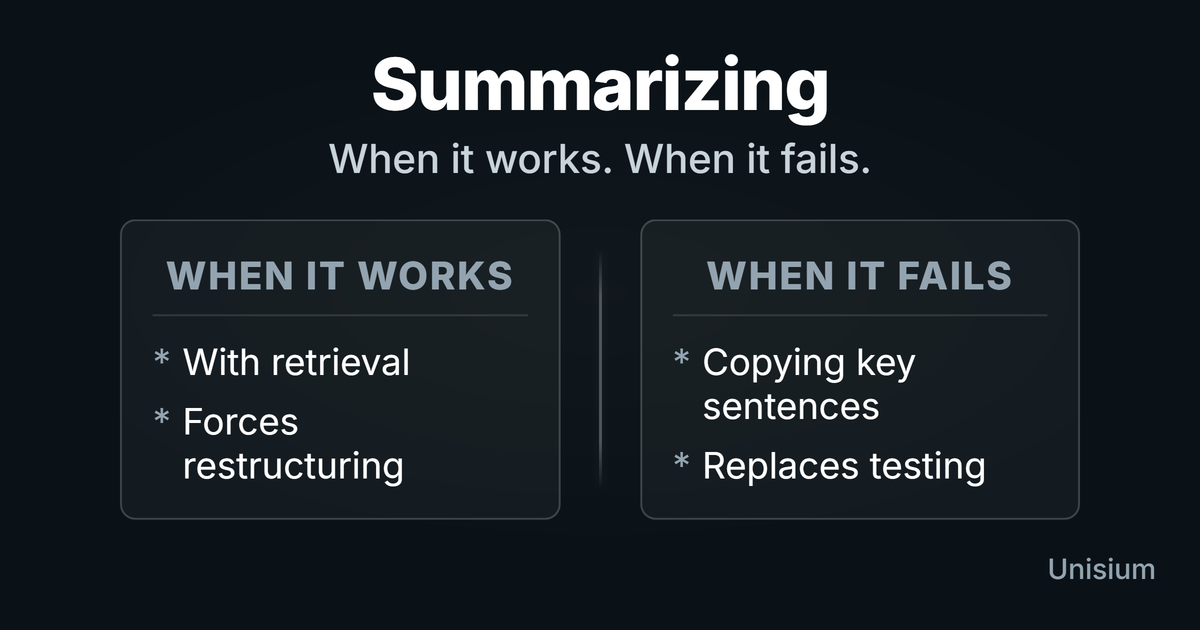
Is summarizing effective for learning math and physics? No
Summarizing feels productive but rarely builds problem-solving skill. Learn when it helps, when it hurts, and what to do instead for durable learning.
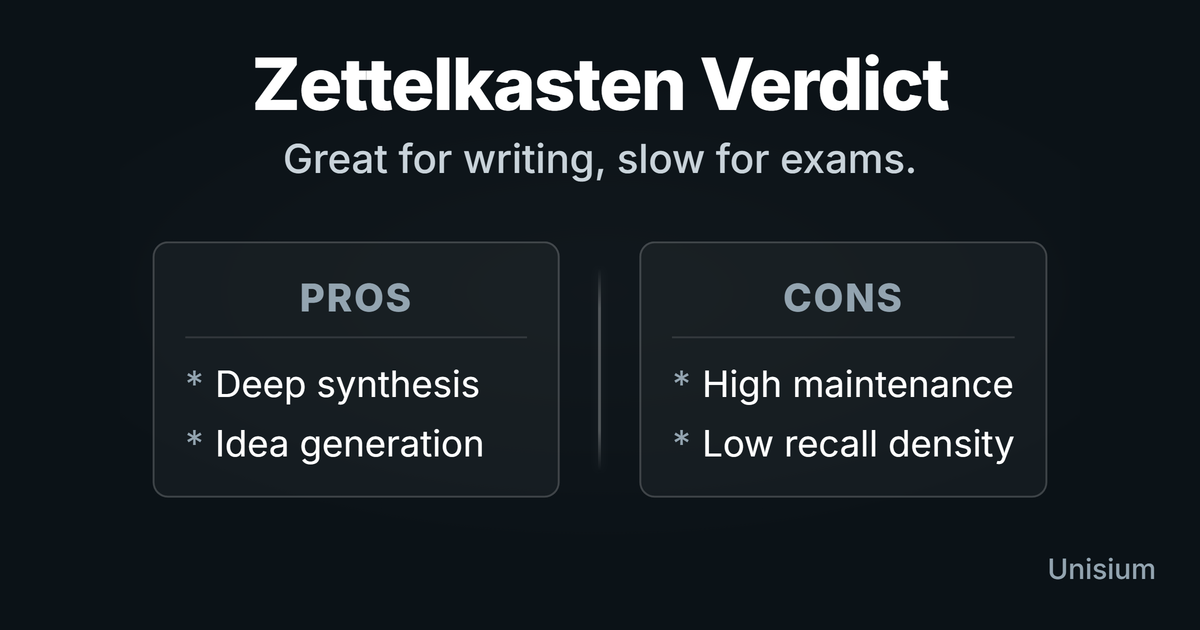
Is Zettelkasten effective for learning math and physics? The efficiency verdict
Zettelkasten helps you connect ideas and write clearer explanations within weeks, but it’s slow for exam fluency. Use it sparingly; solve problems first.

Learning Literature: The Research Behind Effective Study Techniques | Unisium
Evidence-based learning research: ACT-R, retrieval practice, spacing, interleaving, self-explanation. Curated readings behind Masterful Learning.
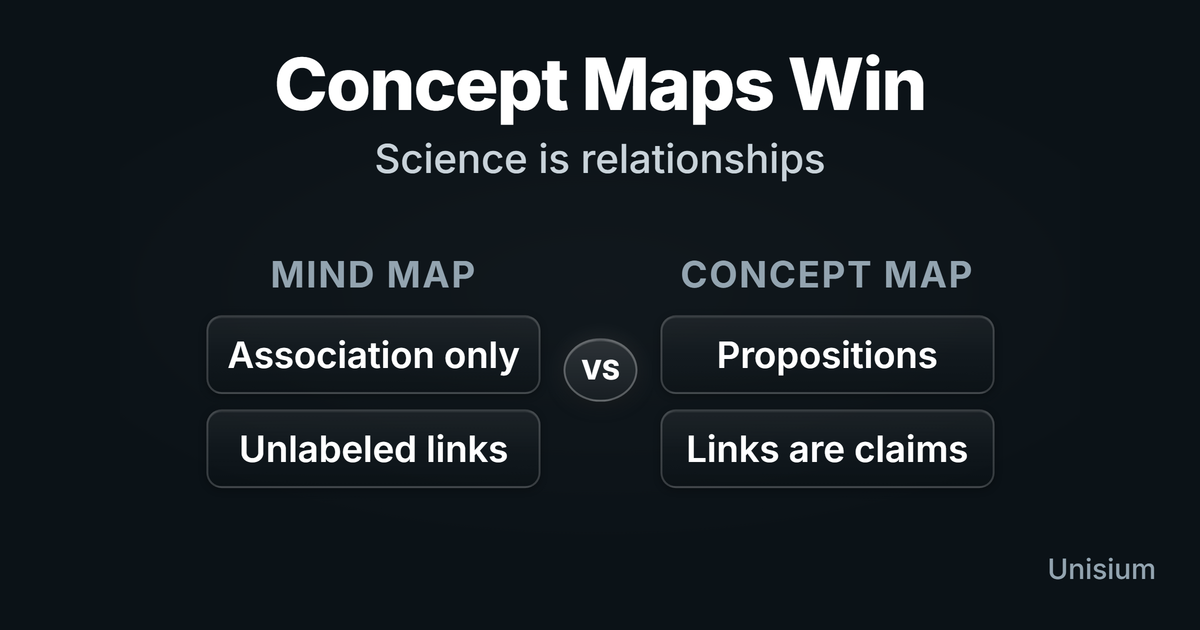
Mind Maps vs Concept Maps: Better for STEM Learning
Mind maps help you generate nodes; concept maps force labeled links. Learn why that structure matters for physics and math, and how to build one fast.

Pomodoro Technique: Focus Tool, Not a Learning Strategy
Is Pomodoro effective for learning? It manages time, not depth. Learn how to adapt it for deep work in physics and math without breaking flow mid-derivation.
Pretesting: Try Before You Know (and Learn Faster)
Pretesting—trying before you know—sharpens attention and upgrades encoding. Use it to amplify elaborative encoding, self-explanation, and problem solving.
Principle Structures: Building Mental Frameworks
Learn how to organize knowledge into powerful mental frameworks that accelerate understanding and retention through hierarchical structures and retrieval practice.
Problem Solving: The Learning Strategy That Turns Knowledge into Skill
Use problem solving as a deliberate learning strategy—not just a homework chore—to convert principles into fluent skills in physics and math.
Retrieval Practice: Make Knowledge Stick (Faster)
Retrieval practice makes principles fast and durable. Learn how to do it—tables, structures, flashcards, spacing, and session flow.

Self-Explanation: Learning from Worked Solutions
Transform worked examples into reliable problem-solving skill through principle-driven explanation and retrievable solution rules.

Spacing vs Cramming: Why Distributed Practice Wins (and Exactly How to Do It)
Stop cramming. Spaced learning builds durable memory, better transfer, and calmer exams. Learn why spacing works—and the exact schedules to use.
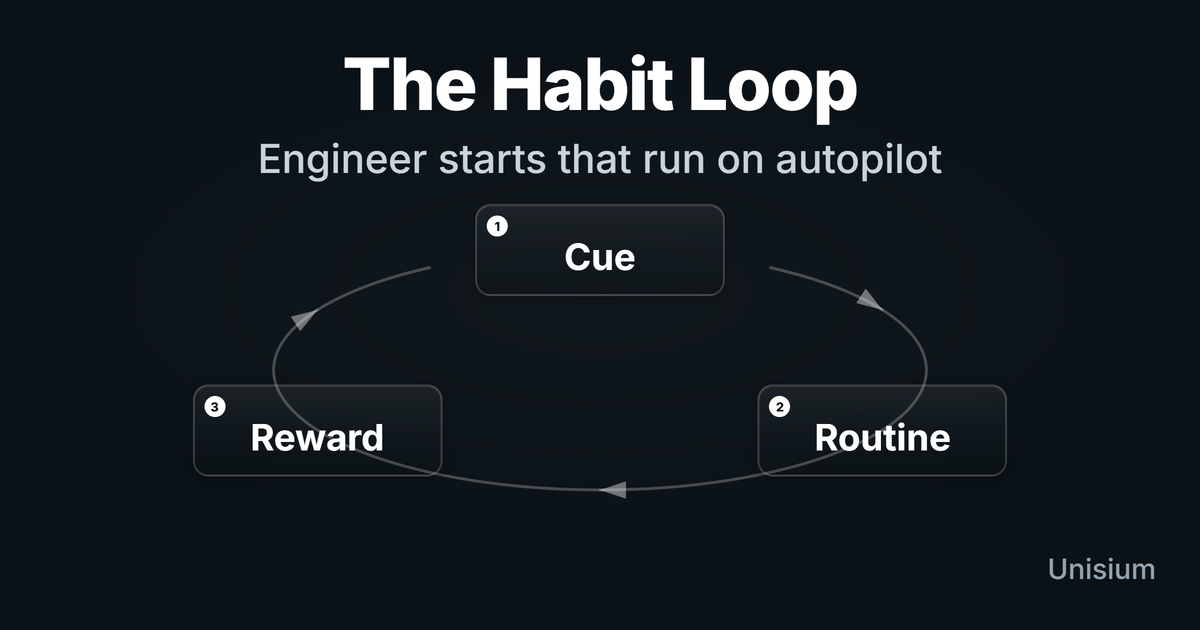
Study Habits for Math and Physics: Start Without Willpower
Study habits are cue-based routines. Learn to write one clear habit rule, engineer cues that trigger studying, and break distractions with friction + replacement.

The Big Learning Myths (That Hold You Back in Math and Physics)
Learning styles, talent, perfect explanations, and neat notes sound comforting—but they quietly wreck your progress in math and physics. Here’s what the research says—and what to do instead.
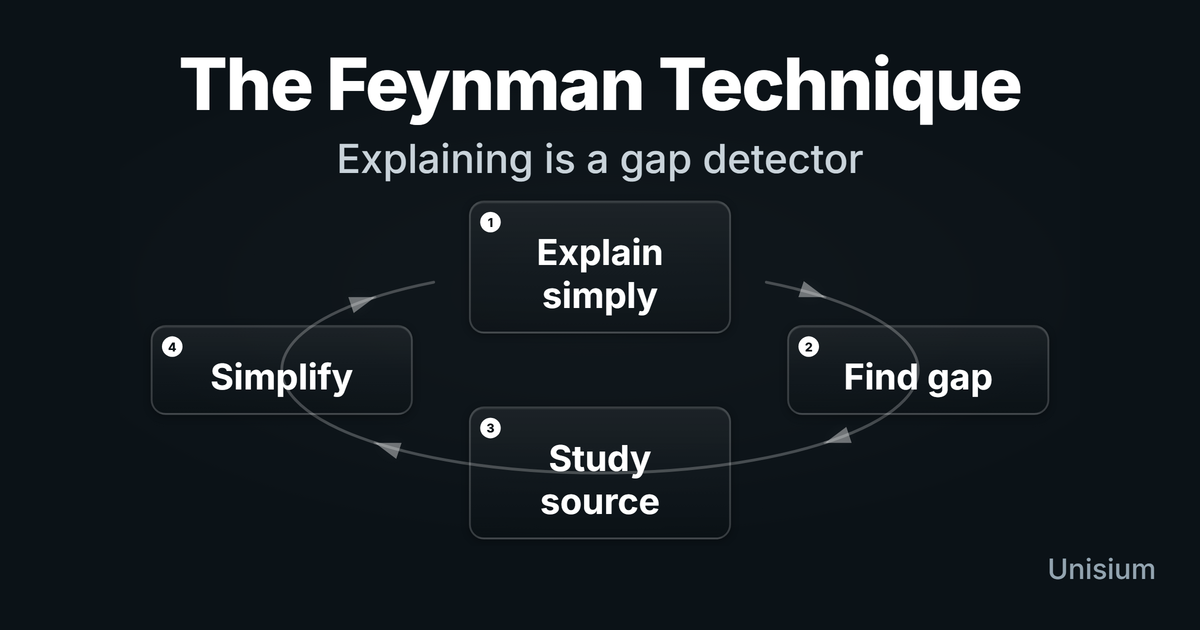
The Feynman Technique: A Gateway to Deep Understanding
Is the Feynman Technique effective? Yes: it forces self-explanation + retrieval, exposing gaps. Use it to simplify tough physics and math concepts for exams.
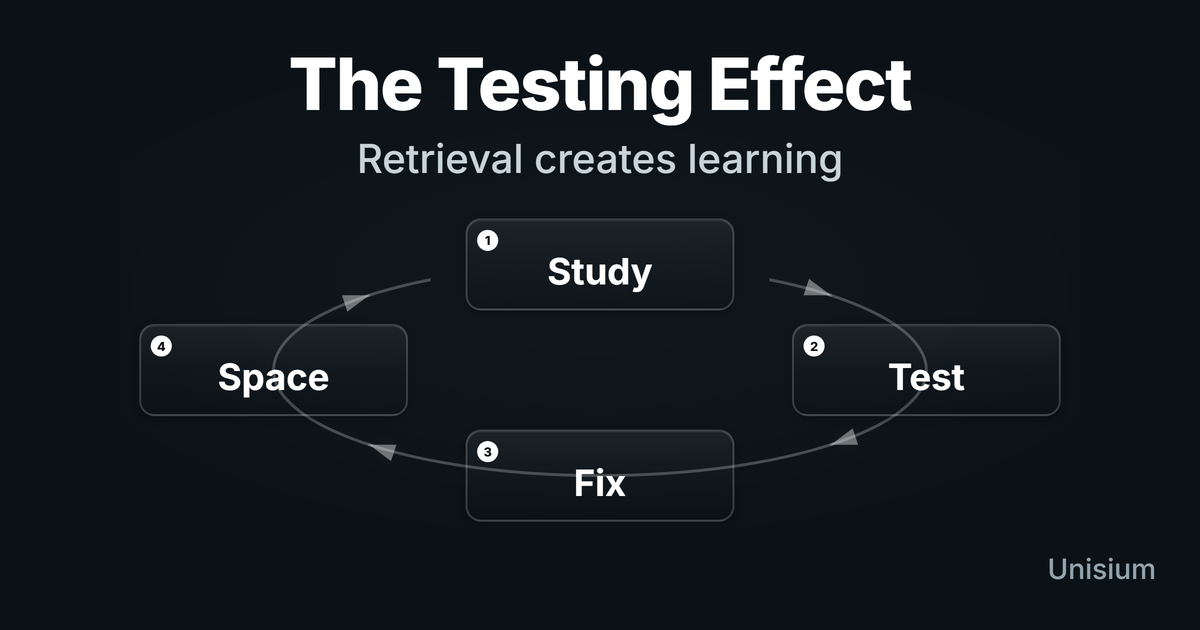
The Testing Effect: How to Supercharge Your Learning by Testing Yourself
Testing yourself isn't just measuring learning—it creates it. Use posttesting + spacing to lock in knowledge and move it to long-term memory.
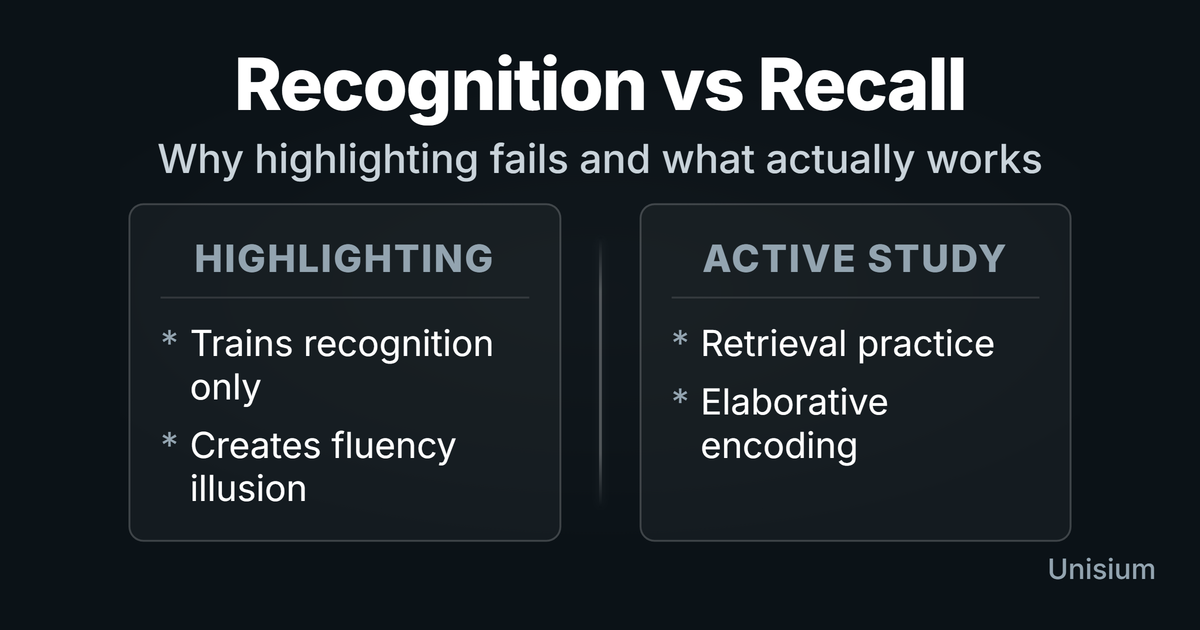
Why Highlighting and Underlining Don't Work (for Learning)
Highlighting feels active but doesn't build recall or transfer. Here's why it fails - and what to do instead that improves learning.
Domain-Specific
Strategies tailored for specific subject areas like physics or math.

After Studying Math and Physics: Stop Consuming, Build
Stop consuming and start creating. Build testable projects, collaborate, get work or research constraints, and pick a mission that makes skills compound.

From Resistance to Flow: Deep Focus for Math and Physics
Learn a repeatable system to enter flow in math and physics: beat the first 3 minutes, calibrate difficulty, and tighten feedback loops.
How to Self-Study Math and Physics Effectively
Build a weekly self-study system for math and physics using four core strategies—elaborative encoding, retrieval practice, self-explanation, and problem-solving.
How to Stay Motivated Studying Math and Physics
Stop waiting for inspiration. Learn how to stay motivated studying math and physics by building competence, autonomy, and relatedness with short feedback loops.
How to Study Physics and Math with AI (Without Letting It Think for You)
Use AI and ChatGPT to learn physics and math faster—by strengthening elaborative encoding, retrieval practice, self-explanation, and problem solving instead of replacing them.

How to Study Physics and Math with Anki (Without Memorizing Trivia)
Stop making 'one fact' flashcards. Learn how to use Anki for elaborative encoding, retrieval practice, and self-explanation in physics and math—and when a dedicated system starts to make more sense.

How to Use Lectures, Workshops, and Other Learning Offers Effectively
Turn lectures, workshops, office hours, and study groups into high-yield learning arenas that support your self-study and your core learning loop.

Is Aesthetic Note-Taking Effective for Math and Physics? Low ROI
Aesthetic notes feel productive but often mask shallow learning. Learn why they fail for problem-solving and how to make them functional without the time cost.

Is study music effective for learning math and physics? Only sometimes
Music can help you start, but lyrics steal working memory for your equations. Use a 10-minute warm-up playlist, then switch to silence for hard problems.

Is the Outline Method effective for learning math and physics? Usually no
Outline Method notes organize definitions fast in one lecture, but hide cross-links needed for derivations. Capture theory, then switch to retrieval practice.
Names Have Power: Why Math and Physics Vocabulary Is Not Optional
From evolution and religion to anime and cognitive science, learn why names have power in math and physics—and how Unisium makes you use the real vocabulary.

Note-Taking During Lectures: Why It Fails (And What Works Instead)
Note-taking during lectures steals attention from reasoning. Learn why it fails and how to replace it with question generation, self-explanation, and problems.

Why Study Math and Physics in the Age of AI?
If AI can already solve problems and write code, is there any point in learning math and physics? Yes—because deep quantitative thinking is the superpower that AI can't replace.

Why You're Not Ready for the Math and Physics Exam (and What to Do Instead)
Most exam prep in math and physics builds either note-based knowledge or blind calculation habits. Learn what written exams test, why your current strategies stall, and how to prepare instead.